Geometry Classes
Geometry Classes#
Note
All Geometry classes are documented in this Google Spreadsheet.
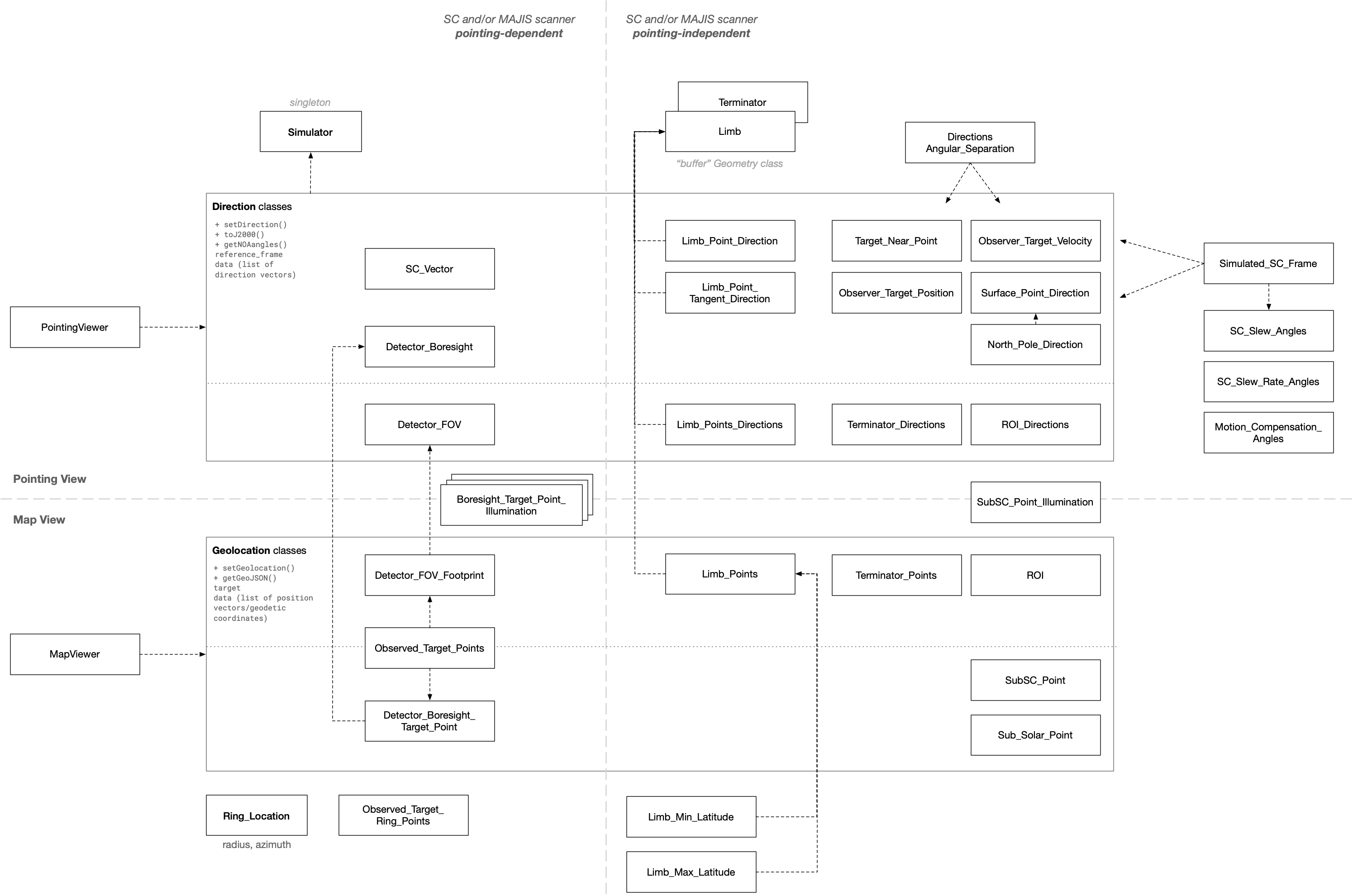
Geometry classes are used to define the geometry and geometrical conditions of a given observation type.
Geometry classes can be of the following types/classes:
Scalar,Vector,Multidimentional, all inheriting from thegfinder.geometry.Geometryclass.A Geometry object can be associated to a GeometryEvent object, which can be an instant acquisition (
Measurement), anObservation, or aSequence.
- Searchable geometries
Only Scalar Geometry objects associated to a Measurement (
measurement_geometriesproperty in ODFs) are “searchable”, and can be used to define geometrical conditions. Exceptions:gfinder.geometry.No_Compensation_Requiredandgfinder.geometry.Scanning_Angleclasses are not searchable.These searchable Geometry objects should primarily be independent of the spacecraft pointing(eg:
gfinder.geometry.SC_Altitude), but can also be pointing-dependent and used during planning activity when the SC pointing is frozen (eg:gfinder.geometry.Target_Point).- Pointing-dependent geometries
Pointing-dependent Geometry classes typically tell us where we are pointing at and what are the illumination conditions; using a given spacecraft pointing baseline (mission scenario), or using a simulated pointing (not yet implemented).
- Direction geometries
“Direction-type” Geometry classes could be used to define simulated pointing (eg:
gfinder.geometry.Limb_Point_Direction), telling us where to point at. See geometrical_models_computation.
