MAJIS Operations Simulator
Contents
MAJIS Operations Simulator#
Overview#
The MAJIS Operations Simulator (MOS) system is being defined and developed. It will consist in a set of interrelated software tools and data accessible and used by the MAJIS team in support to MAJIS Science Operations Planning tasks. The following diagram and description provide a high-level view of the MORS’s main components, external interfaces and data flow. This high-level view/architectural design will evolve with our understanding, and the development, of external interfaces (JUICE SOC Interfaces).
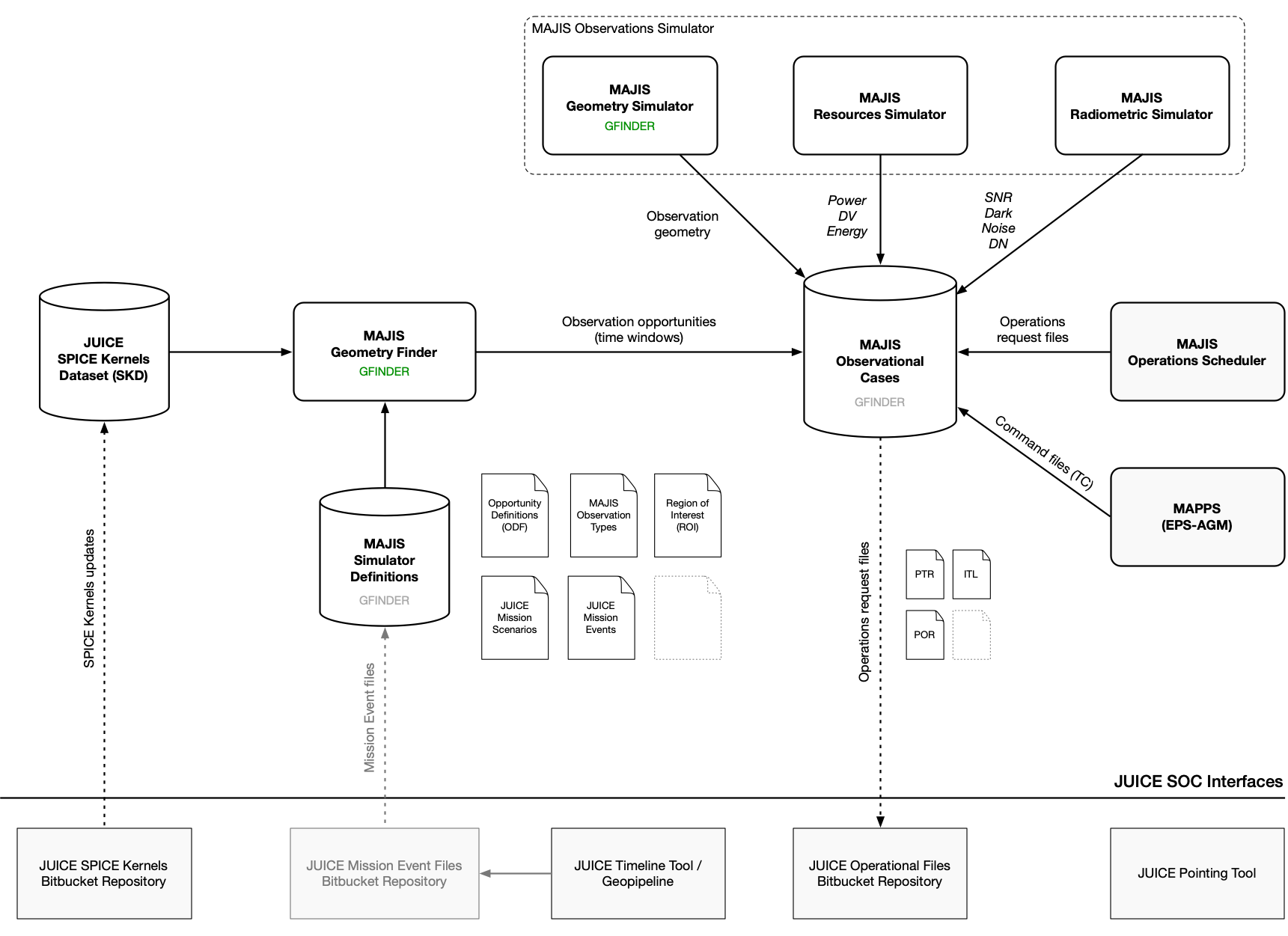
MORS system overview#
Note
As GFINDER is the first MORS system component to be developed and integrated, its design and implementation has lead to provides functions that are intended to be provided by, or shared with, other MORS components in the future. In the above diagram, GFINDER overlaps with the following components:
MAJIS Geometry Finder
MAJIS Geometry Simulator
MAJIS Observations Simulator
MAJIS Observational Cases
MAJIS Simulator Definitions
Components#
- JUICE SPICE Kernels Dataset (SKD)
Provides all the required data for modelling and computing the geometry of the JUICE spacecraft, instruments and targets. It is retrieved and updated from ESS Bitbucket Repository.
- MAJIS Simulator Definitions
[GFINDER] Provides definitions data across all MORS components. Currently: JUICE Mission Scenarios, Mission Events, MAJIS Observation Types, Opportunity Definitions (ODF), Region of Interest (ROI).
- MAJIS Observational Cases
[GFINDER] Stores and manages observational cases data: observation opportunities, observation simulations, and operations requests.
- MAJIS Geometry Finder
[GFINDER] Finds observation opportunities (or opportunity window) given geometrical conditions and time-based constraints over a period of time, mission phase or segment.
- MAJIS Observations Simulator
[GFINDER] Simulate an observation, or sequence of observations, for a given opportunity window and operating parameters.
- MAJIS Geometry Simulator
[GFINDER] Computes geometrical data for a given observation time slot.
- MAJIS Radiometric Simulator
Evaluates the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), dark current, noise and DN for a given observation time slot.
- MAJIS Resources Simulator
Evaluates power, data volume and energy resources for a given observation time slot.
- MAJIS Operations Scheduler
Assembles a collection of simulated observations into an operations plan to be requested. It includes the generation of all required operational files (PTR, ITL, POR, etc…).
- MAPPS (EPS-AGM)
Checks that requested operations are valid, and do not conflict with other instruments and the JUICE spacecraft operations. Commands (TC) are generated (TBC). AGM is the simulator used to calculate and validate the spacecraft attitude while EPS it is used to simulate the spacecraft/instruments operations.
Note
Check MAPPS ANSWERS document from JUICE SOC for more information.
External Interfaces#
- JUICE SPICE Kernels Bitbucket Repository
ESS Bitbucket repository containing a complete set of SPICE Kernels that cover the whole mission lifespan including reconstructed and long term predicted trajectory and orientation.
https://repos.cosmos.esa.int/socci/projects/SPICE_KERNELS/repos/juice
- JUICE Mission Event Files Bitbucket Repository
JUICE SOC Bitbucket repository containing Mission Events files to be used for planning. It includes mission phases and segments for a given mission scenario, as well as time-based constraints for opportunity identification, such as downlink times (DL). See Segment Definitions Report.
Note
Does not exist yet.
- JUICE Timeline Tool
Web application to visualise mission science timeline segmentation, and to provide events overview. Segmentation process is based on geometrical criteria. Generated Mission Events files could be made available through a Bitbucket interface.
- JUICE Operational Files Bitbucket Repository
JUICE SOC Bitbucket repository storing and managing spacecraft and payload operations requests and commands files for all instrument teams.
Note
Does not exist yet.
- JUICE Pointing Tool
Web application to define, validate and visualise pointing and pointing requests (PTR).
Other tools that can be used or useful to science operations planning:
WebGeocalc: Web-based SPICE calculation application and API.
SPICE-enhanced Cosmographia: Desktop 3D Solar System geometry viewer (planet ephemerides, sizes and shapes; spacecraft trajectories and orientations; and instrument field-of-views and footprints).
QGIS /ArcGIS: Desktop Geographic Information Systems (GIS) applications for map/geospatial data visualisation.
Note
Closing-the-loop between uplink and downlink - Downlinked telemetry and subsequent data products should serve as feedback/inputs to future operations planning. For example: the successful observations spatial coverage of a ROI, given certain conditions (eg: illumination, spatial resolution, etc…), should be known in order to target (find opportunities) unobserved areas. Note this apply to any types of ‘scientific’ coverage space (eg for atmospheres: latitude-altitude-solar longitude).
